Gout is a form of arthritis that can cause sudden, severe pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, often affecting the big toe. It occurs due to the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Recognizing the symptoms of gout is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. In this article, we will explore the key indicators of gout, methods of diagnosis, and available treatment options.
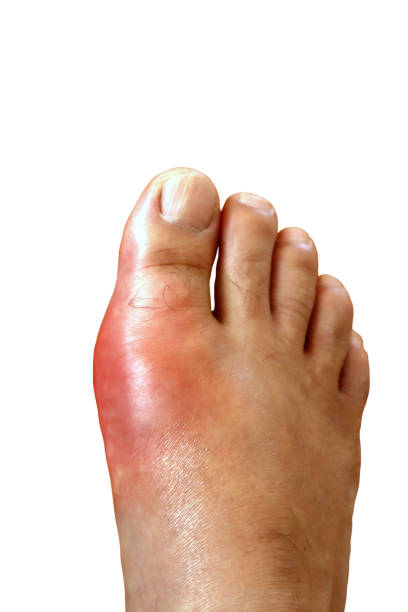
Symptoms Of Gout
- Sudden and Intense Joint Pain: Gout often manifests as abrupt, excruciating pain in one or more joints, typically beginning at night. The pain is usually localized, and it can be so severe that even the weight of a bedsheet can cause discomfort.
- Swelling and Redness: Affected joints become swollen, tender, and red. This is due to the inflammation caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals.
- Limited Range of Motion: As gout progresses, the affected joint’s range of motion may become restricted due to pain and swelling.
- Warmth to the Touch: The skin over the affected joint may feel warm compared to the surrounding areas, indicating increased blood flow and inflammation.
- Recurrent Attacks: Gout often occurs in episodic flare-ups, with symptoms subsiding between attacks. Over time, if left untreated, these attacks may become more frequent and severe.
- Tophi Formation: In advanced cases of gout, small, chalky deposits of urate crystals, known as tophi, can form under the skin around joints and in other tissues. Tophi are a sign that gout has been present for an extended period.
Diagnosing Gout
Diagnosing gout involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, physical examination, and sometimes, specific tests. Here’s a detailed look at the process:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history, including a family history of gout, and conduct a physical examination to assess symptoms and joint involvement.
- Blood Tests: A blood test can measure the levels of uric acid in the blood. Elevated uric acid levels can be indicative of gout, although it’s worth noting that not everyone with high uric acid levels develops gout, and some people with gout have normal uric acid levels.
- Joint Aspiration (Arthrocentesis): This procedure involves removing a small sample of synovial fluid from the affected joint. The fluid is then examined under a microscope for the presence of urate crystals.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans may be used to visualize the affected joints and rule out other potential causes of joint pain and swelling.
- Tophus Examination: If tophi are present, a healthcare provider may extract a sample for microscopic examination to confirm the presence of urate crystals.
Remember, diagnosing gout is a complex process that requires a combination of medical expertise, clinical assessment, and diagnostic tests. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing gout effectively and preventing long-term complications. Seek medical professionals or just simply click on gout specialist melbourne.
Risk Factors For Gout
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing gout. These include:
- Diet: A diet high in purines, found in red meat, seafood, and alcohol, can lead to elevated uric acid levels.
- Obesity: Excess weight can lead to higher levels of uric acid in the blood.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease can increase the risk of gout.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, can raise uric acid levels.
- Family History: Gout tends to run in families.
What Foods Causes Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid in the bloodstream, which can lead to the formation of sharp urate crystals in the joints. Certain foods and beverages are high in purines, which are broken down into uric acid in the body. Consuming excessive amounts of purine-rich foods can lead to elevated uric acid levels and increase the risk of gout attacks. Here are some foods that are commonly associated with triggering gout:
- Organ Meats: Liver, kidneys, and other organ meats are exceptionally high in purines. They should be consumed in moderation by individuals with gout.
- Seafood: Some types of seafood are particularly rich in purines. These include anchovies, sardines, mussels, herring, and trout. It’s advisable to limit the consumption of these items.
- Red Meat: Beef, pork, and lamb are moderately high in purines. Lean cuts and smaller portions may be better choices for those with gout.
- Processed Meats: Foods like hot dogs, sausages, and bacon are not only high in purines but also often contain other additives that can exacerbate gout symptoms.
- Game Meats: Game meats like venison and rabbit tend to be high in purines.
- Alcohol: Beer and spirits, especially beer, are known to increase uric acid levels. Beer contains purines and can also reduce the body’s ability to excrete uric acid.
- Sweetened Beverages: High-fructose corn syrup, commonly found in sugary drinks and fruit juices, has been associated with an increased risk of gout.
- High-Fructose Fruits: Some fruits are relatively high in fructose, which can elevate uric acid levels. Examples include sweetened fruit juices, dried fruits like raisins and dates, and certain high-fructose fresh fruits like apples and pears.
- Yeast-Rich Foods: Yeast extracts, such as those used in certain spreads and gravies, can contribute to higher purine levels.
- Certain Vegetables: While most vegetables are low in purines, some, like spinach, asparagus, and cauliflower, contain moderate levels. However, studies have shown that the impact of vegetable purines on gout is generally much lower compared to animal sources.
It’s important to note that not all individuals with gout will be equally sensitive to purine-rich foods. Some people may be able to consume moderate amounts of these foods without experiencing gout flares, while others may need to be more cautious.
Individuals with gout should consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to create a personalized dietary plan that helps manage uric acid levels and reduces the risk of gout attacks. Additionally, staying well-hydrated, maintaining a healthy body weight, and engaging in regular physical activity are important components of gout management.
Treatment Options For Gout
Medications:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These can help relieve pain and inflammation during gout attacks.
- Colchicine: This medication can be effective in reducing pain and inflammation, particularly in the early stages of an attack.
- Corticosteroids: These may be prescribed in pill form or injected into the affected joint to alleviate severe pain and inflammation.
Urate-Lowering Therapies (ULTs):
These medications, such as allopurinol and febuxostat, work by reducing uric acid production or increasing its excretion from the body. ULTs are used to prevent future gout attacks.
Dietary and Lifestyle Changes:
- Limiting Purine-Rich Foods: Reducing the consumption of foods like organic meats, seafood, and alcohol can help lower uric acid levels.
- Staying Hydrated: Adequate hydration supports kidney function, aiding in the excretion of uric acid.
Weight Management:
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce uric acid levels.
Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve overall joint health and reduce the risk of gout attacks.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of gout and seeking timely medical attention is crucial for the effective management of this painful condition. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and diagnostic processes, individuals can take proactive steps to address gout and improve their quality of life through proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
